HANDBOOKS LIBRARY
FOR RADIATION THERAPY
Serving your Expectation

1. GENERAL OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY
Overview / Principle
Radiation Oncology uses radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. The radiation damages cancer cell DNA so the cell can no longer grow and reproduce. Depending on the type of tumor and the individual case, radiation treatments can be used before surgery to make tumors easier to remove, or afterwards, to make sure no cancer cells are left behind.


2. IMAGING IN RADIOTHERAPY
Patient information is quite important
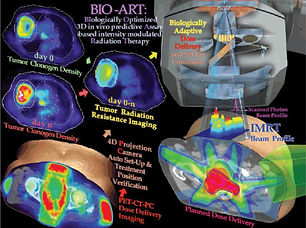
Extension of the image network within radiotherapy departments provides the technical infrastructure which is made necessary by the rapid evolution of techniques in the field of diagnosis and treatment in radiotherapy. The system is aimed at managing the whole set of data (textual data and images) that are needed for planning and control of treatments.
Do it consistent

4. PLANNING
Visualizing your patients
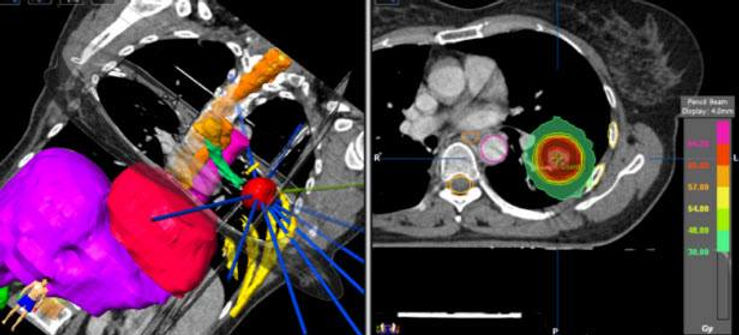
In radiotherapy, radiation treatment planning is the process in which a team consisting of radiation oncologists, radiation therapists, medical physicists and medical dosimetrists PLAN the appropriate external beam radiotherapy or internal brachytherapy treatment technique for a patient with cancer.


5. IMRT
Treatment technique of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced type of radiation therapy used to treat cancer and also non-cancerous tumors. IMRT uses advanced technology to manipulate photon and proton beams of radiation to conform to the shape of a tumor.


6. SRS - SBRT
Stereotactic Radiosurgery & Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) are very effective radiation therapy techniques. These treatment techniques enable a high dose of radiation to be delivered to the cancer cells using a precisely focused method whilst sparing the neighbouring normal cells.

9. TBI
Total Body Irradiation
Total body irradiation (TBI) with megavoltage photon beams is one component used in treating several diseases, including multiple myeloma, leukemias, lymphomas and some solid tumors. TBI provides a uniform dose of radiation to the entire body, penetrating areas such as the central nervous system (CNS) and testes, where traditional chemotherapy is ineffective. The purpose of TBI is threefold: to eliminate residual cancer cells, to provide space for stem cell engraftment through bone marrow depletion, and to prevent rejection of donor stem cells through immunosuppression.